What is oil resistant aviation cable and its core application scenarios?
In the aviation industry, where safety and reliability are non-negotiable, every component plays a critical role in ensuring smooth and secure operations. Among these components, cables are the lifelines that transmit power and signals across various systems of an aircraft. However, the aviation environment is extremely harsh, with exposure to jet fuel, lubricating oils, extreme temperatures, and mechanical stress. This is where oil resistant aviation cable comes into play. Designed to withstand the corrosive effects of oils and fuels while maintaining optimal performance, this specialized cable is a cornerstone of modern aviation systems. In this article, we will delve into the definition, key characteristics, construction materials, and core application scenarios of oil resistant aviation cable, providing valuable insights for professionals in the aviation industry, engineers, and anyone seeking in-depth knowledge about this essential component.
What is Oil Resistant Aviation Cable?
Oil resistant aviation cable, as the name suggests, is a type of specialized cable engineered to resist the degradation caused by exposure to various oils, fuels, and petroleum-based fluids commonly found in aviation environments. Unlike standard cables, which may swell, crack, or lose insulation properties when in contact with oils, this cable is designed to maintain its structural integrity, electrical performance, and mechanical strength even in prolonged exposure to such harsh substances.
At its core, oil resistant aviation cable is not just a single product but a category of cables tailored to meet the stringent requirements of the aviation industry. These requirements are defined by international standards such as FAA (Federal Aviation Administration) specifications, IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards, and MIL-SPEC (Military Specifications), ensuring that the cables meet the highest levels of safety and reliability. For instance, cables used in aircraft must comply with standards like FAA L-824 for airfield lighting systems or MIL-PRF-16173 for corrosion protection coatings, which often include oil resistance as a key criterion.
Key Characteristics of Oil Resistant Aviation Cable
The effectiveness of oil resistant aviation cable stems from a set of key characteristics that make it suitable for the aviation environment:
- Superior Oil and Fuel Resistance: The primary characteristic is its ability to resist swelling, softening, or breaking down when exposed to jet fuel, lubricating oils, hydraulic fluids, and other petroleum-based compounds. This is achieved through specialized insulation and sheath materials that are chemically inert to these substances.
- Wide Temperature Range Tolerance: Aviation cables must operate in extreme temperature conditions, from the frigid cold of high altitudes (-65°C or lower) to the high heat of engine compartments (up to 260°C for some applications). Oil resistant aviation cable is designed to maintain its performance across this wide temperature spectrum without losing flexibility or insulation properties.
- Excellent Electrical Insulation: Maintaining reliable electrical insulation is crucial to prevent short circuits and ensure the safe transmission of power and signals. The insulation materials used in these cables provide high dielectric strength, minimizing the risk of electrical failures.
- Mechanical Durability: Aircraft undergo significant vibration, flexing, and mechanical stress during operation. Oil resistant aviation cable is constructed to be abrasion-resistant, tensile-resistant, and flexible, able to withstand these mechanical forces without damage. For example, some cables are pre-stretched to eliminate rigging and growth changes after installation, ensuring long-term stability.
- Corrosion Resistance: In addition to oil resistance, these cables often feature corrosion-resistant materials (such as stainless steel or galvanized steel conductors) and protective coatings to withstand other harsh environmental factors like salt air (in coastal areas or marine aviation) and humidity.
- Flame Retardancy: Safety in aviation demands that components minimize fire risks. Most oil resistant aviation cables are flame-retardant, designed to prevent the spread of fire and emit low levels of smoke and toxic gases in case of a fire.
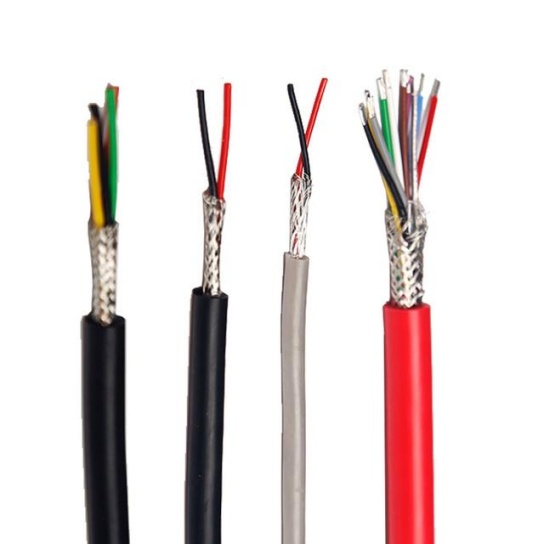
Construction and Materials of Oil Resistant Aviation Cable
The construction of oil resistant aviation cable is a carefully engineered process, with each component selected to contribute to its overall performance. The key components include conductors, insulation, shielding (optional), and sheathing, each made from specialized materials to ensure oil resistance and compliance with aviation standards.
1. Conductors
Conductors are the core of the cable, responsible for transmitting electrical current or signals. The most common materials used for conductors in oil resistant aviation cable are:
- Copper: Often used in stranded form (e.g., rope-stranded copper according to ASTM B-3 & 172) for flexibility. Tinned copper is also popular as it provides additional corrosion resistance, making it suitable for harsh environments.
- Galvanized Steel: Used in some aviation control cables (e.g., Beechcraft cables), galvanized steel offers excellent wear resistance and cost-effectiveness. It is coated with a rust-preventative and lubricating compound to enhance corrosion and oil resistance.
- Stainless Steel: Ideal for applications exposed to salt air, water, or agricultural chemicals (e.g., agricultural aircraft, float planes). While more expensive than galvanized steel, stainless steel provides superior corrosion resistance, though it is softer and more prone to wear at pulleys.
- Nickel-Clad Copper: Used in high-temperature applications (e.g., aircraft engine cables), nickel-clad copper can withstand extreme heat up to 260°C while maintaining conductivity and oil resistance.
2. Insulation Materials
The insulation layer is critical for preventing electrical leakage and protecting the conductor from external factors. Oil resistant aviation cable uses insulation materials that are chemically resistant to oils and fuels, including:
- Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR): Commonly used in medium to high-voltage applications (e.g., 5kV airfield lighting cables), EPR offers excellent oil resistance, wide temperature tolerance (-40°C to +90°C), and good electrical insulation properties.
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): A high-performance material that can withstand extreme temperatures (-65°C to 260°C) and is highly resistant to oils, fuels, and chemicals. PTFE insulation is used in critical applications such as aircraft engine cables and high-frequency signal transmission cables.
- Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE): Provides good oil resistance, high temperature tolerance, and excellent mechanical strength. It is often used in airfield lighting cables and power supply cables for aircraft ground systems.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Modified PVC materials are used for some low-voltage oil resistant cables, offering cost-effectiveness while maintaining adequate oil resistance. However, they are typically limited to lower temperature ranges compared to EPR or PTFE.
3. Sheathing Materials
The outer sheath provides additional protection against mechanical damage, oils, and environmental factors. Common sheathing materials for oil resistant aviation cable include:
- Neoprene: A thermoset material used in 400Hz aircraft ground power cables, neoprene offers excellent oil, ozone, and flame resistance, making it suitable for outdoor and harsh environment applications.
- Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE): Used in FAA L-824 type cables, CPE provides superior oil resistance, abrasion resistance, and UV resistance, making it ideal for airfield lighting systems that are exposed to the elements and potential oil spills.
- Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH): Used in modern aviation cables to minimize smoke and toxic gas emission in case of fire. LSZH sheaths are often combined with polyamide layers to enhance oil resistance, as seen in some fiber optic cables used in aviation fuel systems.
- Polyamide: Known for its excellent chemical resistance, polyamide is used as an inner sheath in some oil resistant cables to provide an additional barrier against oils and fuels, complementing the outer sheath material.
Core Application Scenarios of Oil Resistant Aviation Cable
Oil resistant aviation cable is used in a wide range of applications across the aviation industry, from aircraft on-board systems to ground support equipment. Its ability to withstand oil exposure and harsh conditions makes it indispensable in the following key scenarios:
1. Aircraft Engine Compartments
The engine compartment is one of the harshest environments in an aircraft, with high temperatures, intense vibration, and constant exposure to lubricating oils, hydraulic fluids, and jet fuel. Oil resistant aviation cable is used here for power transmission, signal communication, and control systems. For example, cables like the EN DW A 22 FRF 16 and HFKFPH series are specifically designed for航空发动机内部供电系统连接, with operating temperatures ranging from -60°C to 260°C and superior oil and flame resistance. These cables ensure that critical engine functions, such as fuel injection, ignition, and temperature monitoring, operate reliably even in the presence of oil and extreme heat.
2. Airfield Lighting Systems
Airfield lighting systems, including runway lights, taxiway lights, and obstruction lights, are essential for safe takeoffs and landings, especially in low-visibility conditions. These systems are often exposed to oil spills from aircraft, as well as harsh weather conditions (UV radiation, rain, snow). Oil resistant aviation cables compliant with FAA L-824 standards (such as Type B and Type C cables) are widely used in these systems. These cables feature EPR insulation and CPE or HDPE sheaths, providing excellent oil resistance, UV resistance, and abrasion resistance. They are designed for direct burial or conduit installation, ensuring reliable power supply to lighting fixtures even in oil-contaminated environments. For instance, FAA L-824 Type B unshielded 5kV cables are used to interconnect transformers and current regulators in series lighting circuits, with operating temperatures ranging from -40°C to +85°C.
3. Aircraft Ground Power Supply Systems
Ground power units (GPUs) provide electrical power to aircraft when their engines are not running, enabling maintenance, pre-flight checks, and passenger comfort systems. The cables used in these systems, such as 400Hz moulded ground power cables, must be durable, flexible, and resistant to oil and environmental factors. Prysmian’s 400Hz aviation cable system, for example, features a neoprene outer sheath that is flame, oil, and ozone resistant, making it suitable for indoor and outdoor use in airfields. These cables are designed for quick field replacement and can withstand severe flexing, ensuring a reliable power connection between the GPU and the aircraft even in oil-prone areas.
4. Flight Control Systems
Flight control systems are critical for aircraft maneuverability, and the cables used here must be extremely reliable and resistant to oil and mechanical stress. Control cables, such as elevator control cables and throttle control cables, are often made from galvanized steel or stainless steel with oil-resistant coatings (e.g., MIL-PRF-16173 compound). For example, Beechcraft cables are coated with a modified MIL-PRF-16173 compound that provides additional corrosion and oil resistance beyond standard rust-preventative oils. These cables are pre-stretched and proof-tested to ensure consistent holding strength, ensuring that flight control commands are transmitted accurately even in the presence of oil and vibration.
5. Avionic Systems and Instrumentation
Avionic systems, including navigation systems, communication systems, and flight instruments, rely on precise signal transmission. Oil resistant aviation cable is used here to connect these systems, ensuring that signals are not disrupted by oil exposure or environmental interference. Fiber optic cables with oil-resistant sheaths (e.g., multi-loose tube steel tape armoured jet fuel & oil resistant fibre optic cables) are increasingly used in avionic systems. These cables feature HDPE inner sheaths, polyamide jackets, and LSZH outer sheaths, providing resistance to jet fuels, mineral oils, and other chemicals. They also offer excellent moisture resistance and tensile strength, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor aviation applications.
6. Military and Specialized Aircraft
Military aircraft, such as fighters, bombers, and reconnaissance planes, operate in even harsher environments than civilian aircraft, often exposed to extreme temperatures, combat-related stress, and various oils and fuels. Oil resistant aviation cable used in military applications must meet strict MIL-SPEC standards, ensuring superior performance and durability. For example, stainless steel cables are commonly used in agricultural aircraft and float planes (which are often used in military or special operations) due to their resistance to water and oil. Additionally, specialized cables like the FLVL series, which are lightweight, oil-resistant, and flame-retardant, are used in military aircraft供电系统 to reduce weight while maintaining reliability.
7. Rocket and Satellite Launch Systems
While primarily associated with aircraft, oil resistant aviation cable also plays a role in rocket and satellite launch systems. These systems expose cables to extreme temperatures, high pressure, and rocket fuel (a highly corrosive and flammable substance). Cables like the TYQ series, a special soft light rubber-sheathed cable used for rocket launch ignition lines, are flame-retardant, oil-resistant, and low-temperature resistant, ensuring reliable ignition even in the presence of rocket fuel and extreme conditions. These cables meet the high safety and performance requirements of space launch systems, contributing to the success of rocket and satellite missions.
Conclusion
Oil resistant aviation cable is an indispensable component of the modern aviation industry, designed to withstand the harsh conditions of oil exposure, extreme temperatures, and mechanical stress. Its specialized construction, using high-performance materials for conductors, insulation, and sheathing, ensures that it maintains optimal electrical and mechanical performance in even the most challenging environments. From aircraft engine compartments and airfield lighting systems to ground power supply and avionic systems, this cable plays a critical role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of aviation operations.
As the aviation industry continues to evolve, with advancements in electric aircraft, autonomous flight, and space exploration, the demand for high-performance oil resistant aviation cable will only grow. Manufacturers are constantly innovating, developing cables with improved oil resistance, lighter weight, and higher temperature tolerance to meet the changing needs of the industry. By understanding the definition, characteristics, and applications of oil resistant aviation cable, professionals in the aviation field can make informed decisions when selecting components, ensuring that their systems meet the highest standards of safety and reliability.