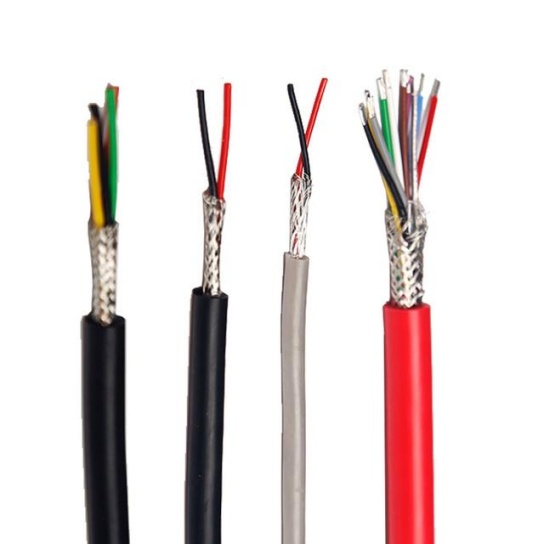
Low-Voltage Aircraft Cable Assemblies for Avionics: Key Considerations for Reliable Performance
Avionics systems—the “brain” of modern aircraft—rely heavily on low-voltage aircraft cable assemblies to transmit critical signals and power between components. Unlike high-voltage cables used for propulsion, these low-voltage assemblies (typically rated under 600V) are designed to support sensitive electronics, from flight control modules to navigation systems. Their performance directly impacts flight safety, system efficiency, and long-term operational reliability, making them a non-negotiable element of avionic design.
1. Core Performance Requirements for Avionic Cable Assemblies
Low-voltage aircraft cable assemblies must withstand the extreme and unique conditions of the aviation environment. Below are the non-negotiable performance criteria:
- Temperature Resistance: Aircraft operate in environments ranging from -65℃ (high-altitude cold) to 150℃ (engine bay heat). Assemblies use insulation materials like PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) or FEP (fluorinated ethylene propylene) to maintain structural integrity and electrical insulation across these temperature extremes.
- Vibration & Shock Tolerance: Continuous vibration during flight and sudden shocks (e.g., turbulence, landing) can damage poorly designed cables. High-quality assemblies feature stranded conductors (instead of solid wires) for flexibility, and robust jacketing to prevent conductor breakage or connector loosening.
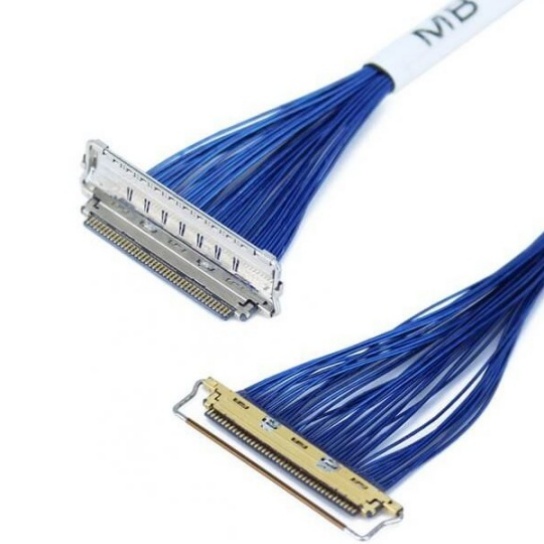
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Shielding: Avionics systems are highly sensitive to EMI from radar, communication devices, or nearby electrical components. Low-voltage cable assemblies often include braided copper shielding or foil layers to block EMI, ensuring signal accuracy and preventing system malfunctions.
- Chemical Resistance: Exposure to aviation fluids (fuel, hydraulic oil, de-icing agents) and atmospheric contaminants (moisture, salt) requires cable jacketing and insulation to resist degradation. Materials like ETFE (ethylene tetrafluoroethylene) are commonly used for their chemical inertness and water resistance.
2. Critical Applications in Avionics
Low-voltage cable assemblies are integrated into nearly every avionic subsystem, where failure could lead to catastrophic consequences. Key applications include:
- Flight Control Systems (FCS): These assemblies transmit low-voltage signals between the cockpit controls (e.g., yoke, pedals) and actuation systems (e.g., flaps, ailerons). Signal delay or distortion here could compromise aircraft maneuverability.
- Navigation & Communication Systems: GPS receivers, inertial navigation units (INUs), and radio transceivers depend on low-voltage cables to send and receive precise data. Shielded assemblies are critical here to avoid EMI-induced signal errors.
- Cockpit Electronics: From multi-function displays (MFDs) to engine monitoring gauges, low-voltage assemblies supply power and transfer data to keep pilots informed. Compact, lightweight designs are prioritized here to save space in the cockpit.
- Auxiliary Systems: Cabin pressure controllers, lighting, and environmental control units (ECUs) also use low-voltage assemblies, where reliability ensures passenger comfort and system longevity.
3. Key Factors for Selection & Sourcing
When selecting low-voltage aircraft cable assemblies for avionics, engineers and procurement teams must prioritize the following to meet industry standards and safety requirements:
- Compliance with Aviation Standards: Assemblies must adhere to global aerospace standards, such as SAE AS39029 (for general-purpose cables), MIL-DTL-24643 (for shielded cables), and EN 3475 (European aviation standards). Compliance ensures compatibility and meets regulatory mandates (e.g., FAA, EASA).
- Material Quality: Conductor materials (e.g., tinned copper, silver-plated copper) affect conductivity and corrosion resistance. Insulation and jacketing materials should be tested for flame retardancy (per FAR 25.853) to prevent fire spread in case of a fault.
- Customization Capabilities: Avionic systems vary by aircraft type (commercial, military, general aviation). Suppliers should offer customizations—such as cable length, connector type (e.g., AMP, TE Connectivity), and shielding configuration—to fit unique system layouts.
- Quality Assurance (QA) Processes: Rigorous testing (e.g., thermal cycling, vibration testing, insulation resistance checks) during manufacturing is essential. Look for suppliers with ISO 9100 certification (aerospace quality management) to ensure consistent quality.
Trust FRS for High-Performance Low-Voltage Avionic Cable Assemblies
When reliability, compliance, and performance matter most for your avionics projects, FRS stands as your trusted manufacturing partner. As a leading factory specializing in aerospace cable assemblies, FRS designs and produces low-voltage solutions that meet SAE, MIL, and EN standards—with every unit undergoing strict thermal, vibration, and EMI testing to ensure airworthiness.
We offer full customization to match your specific avionic system needs, from conductor and insulation material selection to connector integration and shielding design. Our ISO 9100-certified production processes and decades of aerospace experience mean you get cable assemblies that perform consistently, even in the harshest flight conditions. For low-voltage avionic cable assemblies that keep your systems safe and efficient, choose FRS—where precision meets aviation excellence.