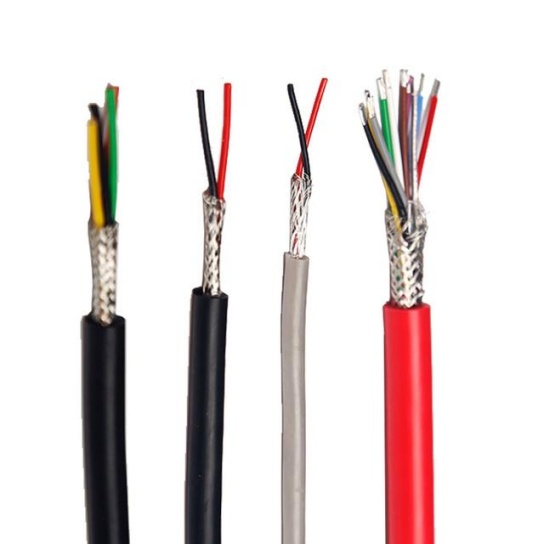
Industry-First Flexible EMI Shielded Aviation Cable Enhances Aircraft Wiring Efficiency
Modern aircraft rely on a vast, intricate network of electrical systems. As avionics, sensors, and high-speed data buses proliferate, the wiring harness becomes not just a component, but a critical system in its own right. In this environment, EMI shielded aviation cableis essential for ensuring signal integrity, safety, and overall aircraft performance.
This article explores the engineering challenges of aircraft EMI, the limitations of traditional shielded cables, and how a new generation of flexible EMI shielded aviation cableis revolutionizing aircraft wiring efficiency.
The Critical Role of EMI Shielding in Aviation
EMI, or electromagnetic interference, is any unwanted electromagnetic energy that can disrupt or degrade the performance of electronic equipment. In aircraft, sources of EMI are numerous:
- Radar and communication systems
- High-current power distribution
- Switching power supplies and motor drives
- Digital avionics and high-speed data buses
EMI can lead to anything from minor data errors to complete system failures, posing serious safety risks. EMI shielded aviation cableis designed to mitigate this by using conductive layers (like braided copper or foil) to create a Faraday cage around internal conductors. This either absorbs or redirects interference, maintaining clean signal transmission for critical systems like flight controls, navigation, and communications .
The Traditional Dilemma: Performance vs. Practicality
Conventional EMI shielded aviation cables, such as those built to MIL-DTL-27500, are highly effective. They feature stranded copper conductors, fluoropolymer insulation, and high-coverage metal braid shields, capable of withstanding temperatures from 150°C to 260°C and voltages up to 600V .
However, these cables face a significant challenge:
- Stiffness vs. Weight:Achieving high shielding effectiveness typically requires thick insulation and dense braiding, which increases both stiffness and weight.
- Routing Difficulties:In the confined spaces of an aircraft, this stiffness makes routing and installation labor-intensive, often requiring specialized tools and connectors.
- Long-Term Reliability:In dynamic areas (e.g., hinged sections, rotating assemblies), repeated bending can fatigue metal shields, leading to degraded performance or failure .
This creates a fundamental conflict: the need for maximum EMI protection versus the need for lightweight, flexible cables that are easy to install and maintain.
The Emergence of Truly Flexible EMI Shielded Aviation Cable
Recent material science and cable engineering have led to a new class of flexible EMI shielded aviation cablethat directly addresses these challenges. These cables are designed to be:
- Highly Flexible:Maintaining a small bend radius for easy routing in tight spaces.
- Lightweight:Utilizing advanced conductors and optimized shielding to reduce overall mass.
- Robust:Withstanding the extreme temperatures, vibration, and fluids common in aerospace environments.
- High-Performing:Providing shielding effectiveness comparable to, or better than, traditional constructions .
Key Innovations
- Advanced Shielding Materials Moving beyond traditional solid copper braids, new designs incorporate lightweight, high-performance alternatives:
- Metallized Textiles:Yarns made of fine aluminum filaments, electroplated for conductivity and corrosion resistance, offer a high strength-to-weight ratio.
- Hybrid Foams:Lightweight carbon nanotube (CNT) and graphene foams provide excellent EMI absorption while remaining extremely light and flexible .
- Optimized Composite Constructions New cables often use a layered approach:
- Conductors:High-strand-count copper or copper alloys for flexibility and current capacity.
- Insulation:Thin, high-performance fluoropolymers (e.g., ETFE, PTFE) that remain flexible at high temperatures.
- Shield:A combination of foil and a lightweight braid, or a textile-based shield, to balance coverage and flexibility.
- Jacket:Abrasion-resistant, chemical-resistant materials like polyurethane (PUR) or PFA .
- Improved Flex-Life Designs are tested for high bend-cycle endurance, ensuring the cable can withstand millions of flexes without degradation. This is crucial for applications like hinged cockpits or deployable structures .
How Flexible EMI Shielded Cables Enhance Wiring Efficiency
The shift to flexible EMI shielded aviation cable delivers tangible benefits across the entire aircraft lifecycle:
1. Simplified Installation & Reduced Labor Costs
The flexibility of these cables allows for tighter bends and more direct routing paths. This reduces the need for complex harness supports and multiple connectors, leading to significant time and cost savings during installation and maintenance .
2. Optimized Weight and Fuel Efficiency
By using lighter shielding materials and thinner constructions, these cables contribute to overall weight reduction. In modern aircraft, where wiring can account for a substantial portion of the empty weight, even small savings per meter can lead to significant fuel burn reductions over the aircraft’s service life .
3. Enhanced Reliability & Safety Margins
The superior flex-life and robust shielding of these cables reduce the risk of in-service failures. This is critical for safety-critical systems where EMI-induced faults can have catastrophic consequences. The improved shielding effectiveness also protects against external threats like lightning and high-intensity radiated fields (HIRF) .
4. Support for Advanced Avionics Architectures
As aircraft adopt more digital systems (e.g., ARINC 664 networks), the demand for high-speed data cables increases. Flexible EMI shielded cables are now available that support Gigabit Ethernet and other high-speed protocols, ensuring clean signal transmission for next-generation avionics .
Practical Considerations for System Designers
When selecting a flexible EMI shielded aviation cable, consider the following:
- EMI Requirements:Define the necessary frequency range and shielding effectiveness (in dB). Higher frequencies may require multi-layer shielding.
- Environmental Conditions:Match the cable’s temperature rating, chemical resistance, and flammability to the specific zone (e.g., cabin, engine bay) .
- Flexing and Bend Radius:For dynamic applications, specify the required flex-life and minimum bend radius. Ensure the cable’s shielding is designed for flexing, not just static installation .
- Connectorization and Grounding:The shield must be properly terminated to the connector backshell and aircraft ground. Follow best practices to avoid ground loops while maintaining a low-impedance path for noise currents .
- Standards and Certification:Ensure the cable meets relevant specifications like MIL-DTL-27500 or EN 3475, and that it is qualified to the necessary flammability and smoke density standards (e.g., ABD0031, FAR/CS-25) .
The Future of EMI Shielding in Aerospace
The development of flexible EMI shielded aviation cableis an ongoing process. Research continues into even lighter, more conductive, and more durable shielding materials, such as advanced nanocarbon composites and smart textiles .
For aircraft manufacturers and operators, the message is clear: upgrading to flexible, high-performance EMI shielded aviation cables is a strategic decision. It leads to tangible improvements in efficiency, reliability, and lifecycle cost, ensuring that critical avionics systems remain protected in an increasingly electromagnetic complex world.