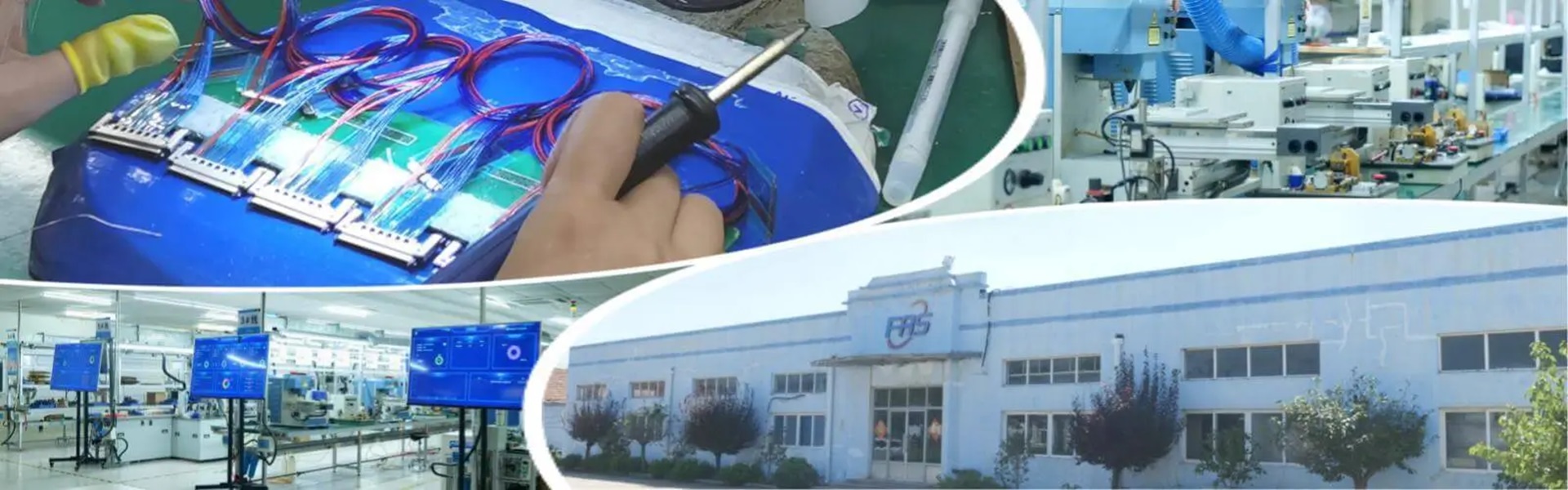
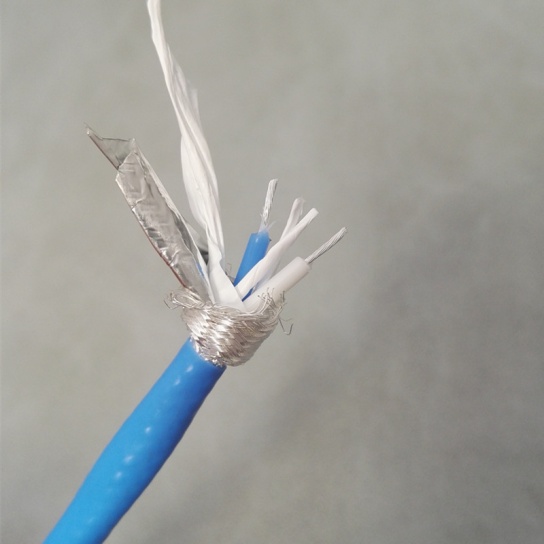
High-Temp Resistant Aviation Electrical Cables: Powering Reliability in Extreme Conditions
When it comes to aviation safety and performance, every component must meet the highest standards—especially electrical systems. High-Temp Resistant Aviation Electrical Cables are engineered to deliver unparalleled durability and reliabi.