Aviation Cables for Satellite Systems: Key Considerations, Applications, and Reliability Standards
Satellite systems are the backbone of modern communication, navigation, weather forecasting, and space exploration—relying on components that can withstand the harshest environments, from extreme temperatures and radiation in orbit to mechanical stress during launch. Among these critical components, aviation cables for satellite systems stand out as unsung heroes: they transmit power, data, and signals between satellite subsystems (such as solar panels, batteries, transponders, and antennas) with zero margin for failure. Unlike standard industrial cables, these specialized cables must meet rigorous performance criteria to ensure mission success, as even a minor cable malfunction can lead to costly satellite downtime or complete mission failure.
In this article, we’ll dive into the core requirements, common applications, 选型 essentials, and reliability standards for aviation cables in satellite systems—providing practical insights for engineers, procurement teams, and aerospace professionals tasked with building or maintaining satellite infrastructure.
1. Critical Technical Requirements for Satellite-Grade Aviation Cables
Satellite systems operate in environments that push materials to their limits. Whether in geostationary orbit (GEO), low Earth orbit (LEO), or deep space missions, aviation cables must address four primary challenges: extreme environmental conditions, minimal weight and size, signal integrity, and long-term reliability.
a. Resistance to Extreme Temperatures and Radiation
Satellites experience temperature fluctuations ranging from -150°C (-238°F) in the shadow of Earth to +120°C (+248°F) when exposed to direct sunlight. Aviation cables for satellite systems must use insulation and jacket materials that remain flexible and functional across this broad range—common options include PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), FEP (fluorinated ethylene propylene), and PFA (perfluoroalkoxy alkane). These fluoropolymers offer excellent thermal stability, low outgassing (critical to prevent contamination of satellite optics and sensors), and resistance to thermal cycling.
Additionally, space is flooded with ionizing radiation (solar flares, cosmic rays, and Van Allen radiation belts), which can degrade cable materials and disrupt signal transmission. Satellite-grade cables are manufactured with radiation-resistant materials and shielding (such as braided stainless steel or aluminum) to minimize radiation-induced damage, ensuring consistent performance over the satellite’s operational lifespan (typically 10–15 years).
b. Lightweight and Compact Design
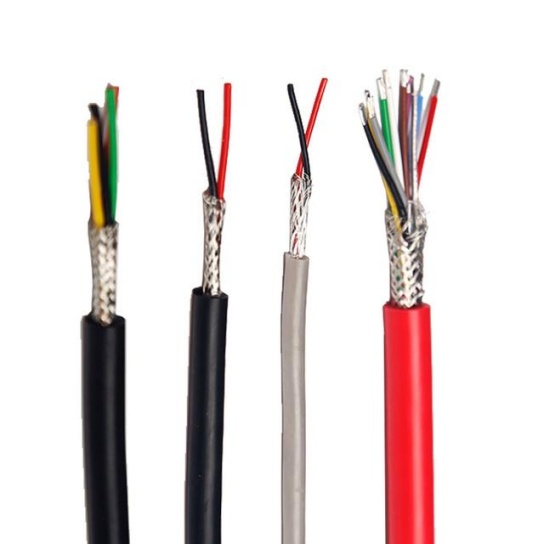
Every gram matters in satellite design—launch costs are measured per kilogram, and space inside the satellite bus is limited. Aviation cables for satellite systems are engineered to be lightweight yet durable, using thin-walled insulation, high-strength conductors (such as copper-clad aluminum or pure copper with optimized stranding), and compact shielding configurations. For example, micro-coaxial cables or twisted-pair cables with minimal insulation thickness are often used for signal transmission, while power cables balance current-carrying capacity with weight reduction.
c. Signal Integrity and Low Loss
Satellite systems rely on precise data and signal transmission—from high-frequency communication signals (e.g., Ka-band, Ku-band) to low-voltage power signals for sensitive electronics. Aviation cables must minimize signal attenuation (loss) and electromagnetic interference (EMI) to ensure accurate data transfer. Key features include:
- Low dielectric constant (εr) of insulation materials to reduce signal delay and loss.
- EMI shielding (braided, foil, or combination shields) to block external interference and prevent signal leakage.
- Impedance matching (e.g., 50Ω for RF cables, 100Ω for twisted-pair data cables) to avoid signal reflection.
d. Mechanical Durability and Vibration Resistance
During launch, satellites endure intense vibrations, shock, and acceleration (up to 20g or more). Aviation cables must withstand these mechanical stresses without breaking, cracking, or losing connectivity. This requires robust conductor stranding (e.g., stranded copper for flexibility), strong insulation-jacket bonding, and strain relief features at cable terminations. Additionally, cables must resist abrasion and wear from contact with other satellite components during launch and in orbit.
2. Common Applications of Aviation Cables in Satellite Systems
Aviation cables for satellite systems are tailored to specific subsystems, each with unique requirements. Below are the most critical applications:
a. Power Distribution Cables
Satellites generate power via solar panels and store it in batteries—power distribution cables must transmit this power efficiently to all subsystems (e.g., transponders, attitude control systems, and communication antennas). These cables are designed for high current-carrying capacity (typically 10–100A) with low resistance to minimize power loss. They often use multi-stranded copper conductors and PTFE/FEP insulation to handle high temperatures and prevent overheating.
b. Communication and RF Cables
Satellite communication relies on high-frequency RF (radio frequency) cables to transmit signals between transponders and antennas. These cables must support frequencies ranging from MHz to GHz (e.g., L-band, C-band, Ka-band) with minimal signal loss. Common types include semi-rigid coaxial cables, flexible coaxial cables, and waveguide cables—all engineered with low-loss dielectrics and precision shielding to maintain signal integrity over long distances (relative to satellite size).
c. Data and Control Cables
Satellite subsystems communicate via digital data cables (e.g., Ethernet, CAN bus, or custom protocols) to coordinate operations, send telemetry data to Earth, and receive commands. These cables prioritize low EMI, high data rates (up to 10Gbps or more for modern satellites), and reliability. Twisted-pair cables with foil/braid shielding are common, as they balance flexibility and noise resistance.
d. Thermal Control Cables
Some satellites use thermal control systems (e.g., heaters, heat pipes) to regulate temperature—thermal control cables transmit power to these systems and send temperature sensor data to the satellite’s central computer. These cables are designed to operate in extreme temperature gradients and resist corrosion from exposure to space debris or atomic oxygen.
3. Key Considerations for Selecting Aviation Cables for Satellite Systems
Choosing the right aviation cables for a satellite mission requires balancing technical performance, compliance, and mission-specific needs. Here are the top factors to evaluate:
a. Compliance with Aerospace Standards
Satellite components are subject to strict industry standards to ensure reliability and compatibility. Key standards for aviation cables include:
- NASA’s GSFC (Goddard Space Flight Center) specifications (e.g., GSFC-STD-6000) for spaceflight hardware.
- ESA (European Space Agency) standards (e.g., ECSS-Q-ST-20-07C) for materials and components.
- MIL-DTL (Military Specification) standards (e.g., MIL-DTL-17F for coaxial cables, MIL-DTL-27500 for insulated wires) for aerospace-grade performance.
Ensure that cables meet or exceed these standards—non-compliant cables may fail qualification testing or pose mission risks.
b. Environmental Compatibility
Consider the satellite’s orbit and mission duration:
- LEO satellites (200–2,000km altitude) face more atmospheric drag and radiation than GEO satellites—cables must be more robust against wear and radiation.
- Deep space missions (e.g., Mars rovers, lunar orbiters) require cables with extreme temperature resistance (-200°C to +150°C) and radiation hardening.
- Outgassing is critical for all space missions—cables must meet NASA’s ASTM E595 standard for low outgassing to avoid contaminating sensitive optics or solar panels.
c. Conductor and Insulation Materials
- Conductors: Copper is preferred for its high conductivity, but copper-clad aluminum (CCA) offers weight savings (ideal for LEO satellites). For high-temperature applications, nickel-plated copper conductors provide corrosion resistance.
- Insulation/Jacket: PTFE, FEP, and PFA are the gold standards for space applications—avoid materials like PVC (which outgasses and degrades in extreme temperatures). For mechanical strength, consider cables with a dual-layer insulation (e.g., FEP inner + PFA outer).
d. Shielding Requirements
EMI shielding is critical for satellite cables, as interference can disrupt communication or data transmission. Choose shielding based on the application:
- Foil shielding (aluminum or copper foil) for lightweight, flexible cables (e.g., data cables).
- Braided shielding (stainless steel or copper braid) for high EMI protection (e.g., RF cables).
- Combination shielding (foil + braid) for maximum noise resistance (e.g., critical control cables).
e. Customization for Mission-Specific Needs
No two satellite missions are identical—look for cable manufacturers that offer customization, such as:
- Custom conductor sizes and stranding to meet current or flexibility requirements.
- Tailored insulation thickness for space constraints.
- Specialized shielding or jacketing for extreme environments (e.g., atomic oxygen resistance for LEO satellites).
4. Reliability Testing and Quality Assurance for Satellite-Grade Cables
Aviation cables for satellite systems undergo rigorous testing to ensure they can withstand the demands of space. Key tests include:
- Thermal cycling: Exposing cables to repeated temperature extremes (-150°C to +120°C) to check for insulation cracking or conductor fatigue.
- Radiation testing: Subjecting cables to gamma rays or proton radiation to verify radiation resistance and signal integrity.
- Vibration and shock testing: Simulating launch conditions to ensure cables survive mechanical stress.
- Outgassing testing: Measuring volatile organic compounds (VOCs) to comply with ASTM E595.
- Signal loss testing: Evaluating attenuation at mission-specific frequencies to ensure data/communication reliability.
Quality assurance is equally critical—reputable manufacturers use traceable materials, implement strict quality control processes (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100 for aerospace), and provide detailed test reports for each cable batch.
5. FRS: Your Trusted Partner for Satellite-Grade Aviation Cables
When it comes to aviation cables for satellite systems, reliability, compliance, and performance are non-negotiable—and FRS Brand Factory delivers on all three. As a leading manufacturer of aerospace-grade cables, FRS specializes in engineering custom solutions tailored to the unique demands of satellite missions, from LEO communication satellites to deep space exploration vehicles.
FRS’s satellite-grade aviation cables meet or exceed NASA, ESA, and MIL-DTL standards, with radiation-resistant materials, low-outgassing insulation, and precision shielding to ensure signal integrity and durability in extreme space environments. Our team of aerospace engineers collaborates with clients to customize conductor sizes, insulation materials, and shielding configurations—optimizing weight, space, and performance for your mission.
Every FRS cable undergoes rigorous testing, including thermal cycling, radiation exposure, and vibration testing, to guarantee reliability over 10–15+ year operational lifespans. Whether you need power distribution cables, high-frequency RF cables, or data control cables, FRS delivers consistent quality and technical support to keep your satellite mission on track.
For satellite systems that demand uncompromising performance, choose FRS Brand Factory—where aerospace expertise meets precision engineering. Contact us today to discuss your custom cable requirements and elevate your satellite’s reliability.