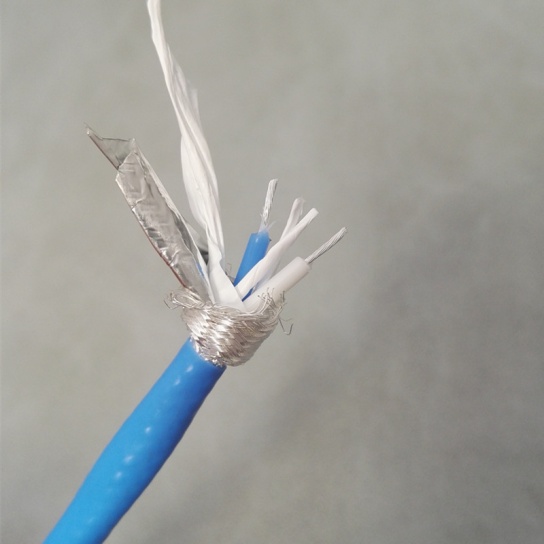
Aviation Cables for ELT
In the dynamic and safety-critical world of aviation, every component plays a pivotal role in ensuring the security of flights and the lives on board. Among these components, Emergency Locator Transmitters (ELTs) stand out as a vital lifeline in emergency situations. ELTs are designed to automatically transmit distress signals when an aircraft experiences an accident or emergency, enabling search and rescue teams to locate the aircraft quickly. However, the effectiveness of an ELT system hinges on a often-overlooked yet indispensable element: Aviation Cables for ELT. These cables serve as the backbone of ELT systems, facilitating the seamless transmission of signals and power, making them a non-negotiable part of aviation safety infrastructure.
The Critical Role of Aviation Cables in ELT Systems
ELT systems operate in some of the most demanding conditions imaginable, from extreme temperatures and剧烈 vibrations to exposure to harsh chemicals and moisture. For an ELT to function reliably when it matters most, the aviation cables connecting its various components—such as the transmitter, antenna, power source, and activation sensors—must be capable of withstanding these harsh environments while maintaining uncompromised performance. Aviation Cables for ELT are specifically engineered to meet these rigorous demands, ensuring that the distress signals generated by the ELT are transmitted clearly and efficiently to search and rescue satellites or ground stations.
One of the primary functions of Aviation Cables for ELT is signal transmission. When an emergency occurs, the ELT’s transmitter generates a distress signal, typically on the 121.5 MHz (civilian) or 243.0 MHz (military) frequency bands, or the newer 406 MHz band which offers better satellite coverage. These signals must travel through the aviation cables to the antenna, which then broadcasts them into the atmosphere. Any interference, signal loss, or degradation in the cables can result in delayed or missed detection by search and rescue teams, putting lives at risk. Thus, the cables must have excellent signal integrity, minimizing attenuation and electromagnetic interference (EMI) to ensure the signals reach their intended destination with clarity.
In addition to signal transmission, Aviation Cables for ELT also play a crucial role in power delivery. ELTs are powered by either the aircraft’s main electrical system or dedicated backup batteries. The cables must efficiently carry the required electrical current to the ELT’s transmitter and other components, ensuring that the system remains operational even in the event of a main power failure. This requires the cables to have low electrical resistance, high current-carrying capacity, and robust insulation to prevent short circuits or power leaks, which could disable the ELT when it is most needed.
Core Characteristics of High-Quality Aviation Cables for ELT
Given the critical nature of their application, Aviation Cables for ELT must adhere to strict industry standards and possess a set of key characteristics that enable them to perform reliably in aviation emergencies. These characteristics are not just desirable but mandatory, as they directly impact the safety and effectiveness of the ELT system.
1. Temperature Resistance
Aircraft operate in a wide range of temperatures, from the extreme cold of high altitudes (which can drop to -55°C or lower) to the intense heat generated by engine compartments or during an emergency landing (which can exceed 150°C). Aviation Cables for ELT must be able to withstand these temperature extremes without degradation of their insulation, conductors, or shielding. High-quality cables use materials such as fluoropolymers (e.g., PTFE, FEP) for insulation, which offer excellent thermal stability, resisting melting, cracking, or brittleness even in the most extreme temperature conditions. This ensures that the cables maintain their electrical and mechanical properties, keeping the ELT system operational when temperatures fluctuate drastically.
2. Vibration and Shock Resistance
Aircraft are subject to constant vibrations during flight, from the rotation of engines to turbulence. In the event of an emergency, such as a crash or hard landing, the ELT system and its cables may experience severe shock loads. Aviation Cables for ELT must be designed to withstand these vibrations and shocks without becoming damaged or disconnected. This is achieved through the use of robust conductor stranding (e.g., multiple strands of tinned copper wire, which are more flexible and resistant to fatigue than solid conductors) and durable jacket materials that can absorb and dissipate vibration energy. Additionally, the cables are often reinforced with braided shielding or armor layers to provide extra protection against mechanical stress, ensuring that the electrical connections remain intact even in the most turbulent or impactful situations.
3. Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Aviation environments expose cables to a variety of harsh chemicals, including jet fuel, hydraulic fluids, lubricants, and cleaning agents. These chemicals can degrade ordinary cables, causing their insulation or jackets to swell, crack, or dissolve, which can lead to electrical failures. Aviation Cables for ELT are constructed with chemical-resistant materials that repel these substances, maintaining their structural integrity and electrical performance. For example, the outer jacket may be made of polyurethane or ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), which are known for their resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents. Additionally, the cables are designed to resist moisture, humidity, and UV radiation, which can also cause degradation over time. This ensures that the cables remain reliable even in damp or exposed environments, such as when an aircraft is submerged in water or left exposed to the elements after an emergency.
4. Electrical Performance Stability
Consistent electrical performance is essential for Aviation Cables for ELT, as any variation in impedance, capacitance, or resistance can affect signal transmission. High-quality cables are manufactured with precise conductor dimensions and uniform insulation thickness to ensure stable electrical properties across a wide range of operating conditions. They also feature effective shielding, such as braided copper or aluminum foil, to protect against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) from other aircraft systems, such as radar, communication radios, or navigation equipment. EMI/RFI can distort the ELT’s distress signal, making it difficult for search and rescue teams to detect or decode. By minimizing interference, the shielding ensures that the ELT’s signal remains clear and identifiable, increasing the chances of a timely rescue.
5. Compliance with Aviation Standards
Aviation Cables for ELT must meet stringent industry standards and regulations to ensure their safety and reliability. These standards are set by organizations such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States, the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) in Europe, and the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) globally. Standards such as SAE AS22759 (for aerospace cables) and MIL-DTL-24643 (military specification for aircraft cables) outline specific requirements for conductor materials, insulation thickness, temperature range, flame resistance, and mechanical performance. Compliance with these standards is not just a legal requirement but also a testament to the cable’s quality and suitability for use in aviation ELT systems. Manufacturers must undergo rigorous testing and certification processes to ensure their cables meet these standards, giving aircraft operators confidence in their performance.
Types of Aviation Cables for ELT Applications
There are several types of Aviation Cables for ELT, each designed to meet specific application requirements and environmental conditions. The choice of cable type depends on factors such as the ELT system’s design, the location of the components within the aircraft, and the expected operating conditions.
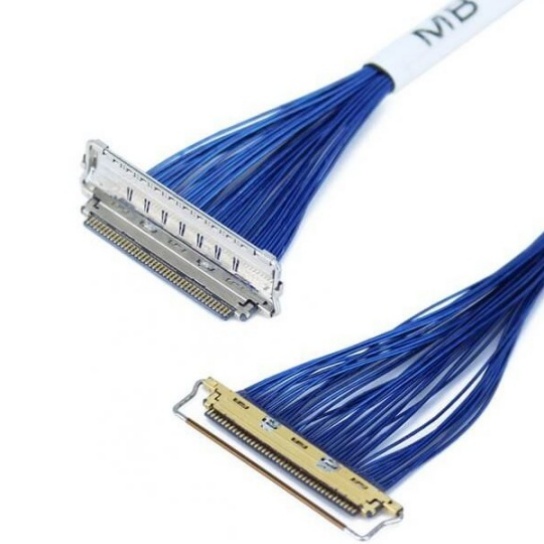
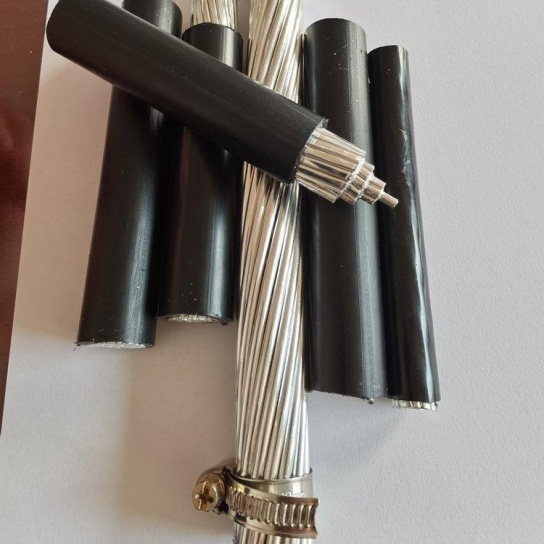
1. Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables are commonly used for connecting the ELT transmitter to the antenna, as they are ideal for transmitting high-frequency signals with minimal loss. A typical coaxial cable consists of a central conductor (usually a stranded copper wire), an insulating layer (e.g., PTFE), a conductive shield (braided copper or foil), and an outer jacket (e.g., FEP or polyurethane). The shield provides excellent EMI/RFI protection, ensuring that the ELT’s signal is not distorted during transmission. Coaxial cables for ELT applications are often rated for high temperatures and harsh environments, making them suitable for installation in engine compartments or other areas exposed to extreme conditions.
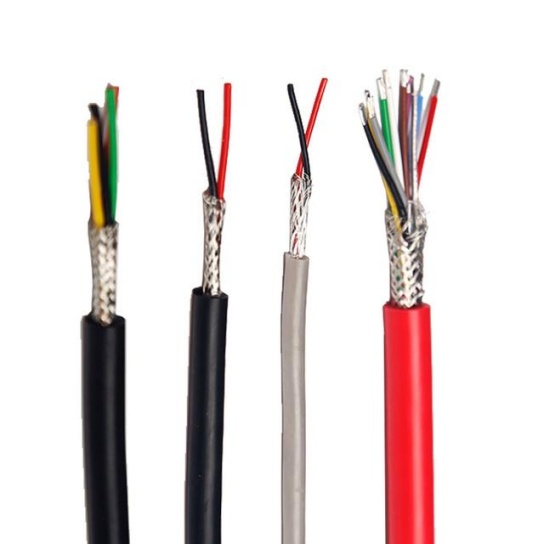
2. Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted pair cables consist of two insulated conductors twisted together, which helps to reduce crosstalk and EMI. They are sometimes used for connecting ELT activation sensors to the transmitter, as they can transmit low-voltage signals reliably over short distances. Twisted pair cables for aviation applications are available in shielded and unshielded versions; shielded twisted pair (STP) cables offer additional protection against interference, making them a better choice for ELT systems where signal integrity is critical.
3. Power Cables
Power cables are used to supply electrical current from the aircraft’s main power system or backup batteries to the ELT. These cables are designed to carry higher currents than signal cables, so they have larger conductors and thicker insulation to prevent overheating and short circuits. Power cables for ELT applications are often made with tinned copper conductors for corrosion resistance and flexible stranding for ease of installation. They may also feature flame-retardant jackets to comply with aviation safety standards, which require cables to resist burning and prevent the spread of fire in the event of an emergency.
Key Considerations When Choosing Aviation Cables for ELT
Selecting the right Aviation Cables for ELT is a critical decision that can impact the safety and reliability of the aircraft’s emergency systems. Aircraft operators, maintenance teams, and system integrators should consider the following factors when choosing these cables:
- Environmental Conditions: Evaluate the temperature range, vibration levels, chemical exposure, and moisture conditions where the cables will be installed. Choose cables that are specifically rated to withstand these conditions to ensure long-term reliability.
- Signal and Power Requirements: Determine the frequency of the ELT signal and the current requirements of the system. Select coaxial cables with the appropriate impedance (typically 50 ohms for aviation RF applications) for signal transmission, and power cables with the correct conductor size to handle the required current.
- Compliance with Standards: Ensure that the cables meet all relevant aviation standards, such as FAA, EASA, or SAE specifications. Non-compliant cables may not perform as expected in emergencies and could lead to regulatory violations.
- Installation and Flexibility: Consider the installation route and space constraints within the aircraft. Choose cables that are flexible enough to be routed through tight spaces without damaging the insulation or conductors. Additionally, look for cables with durable jackets that can withstand the wear and tear of installation and maintenance.
- Manufacturer Reputation: Select cables from a reputable manufacturer with a proven track record in the aviation industry. A reliable manufacturer will provide detailed documentation, including test reports and certification, to verify the cable’s performance and compliance with standards.
FRS: Your Trusted Partner for High-Quality Aviation Cables for ELT
When it comes to Aviation Cables for ELT, there is no room for compromise on quality, reliability, or compliance. At FRS, we understand the critical role these cables play in aviation safety, and we are committed to manufacturing products that meet the highest industry standards and exceed our customers’ expectations.
As a leading brand factory specializing in aviation cables, FRS combines decades of engineering expertise with state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities to produce Aviation Cables for ELT that are built to perform in the most demanding environments. Our cables are constructed using premium materials, including high-purity tinned copper conductors, fluoropolymer insulation, and chemical-resistant jackets, ensuring exceptional temperature resistance, vibration tolerance, and signal integrity. We adhere strictly to global aviation standards, such as SAE AS22759, MIL-DTL-24643, and EASA requirements, and every batch of cables undergoes rigorous testing—including temperature cycling, vibration testing, chemical exposure testing, and electrical performance analysis—to ensure compliance and reliability.
At FRS, we don’t just manufacture cables; we provide tailored solutions to meet the unique needs of our customers. Our team of experienced engineers works closely with aircraft operators, ELT system integrators, and maintenance teams to design cables that fit specific installation requirements, whether it’s for a commercial airliner, a military aircraft, or a general aviation vehicle. We offer a wide range of cable types, including coaxial cables, twisted pair cables, and power cables, all customizable to meet varying signal, power, and environmental demands.
When you choose FRS Aviation Cables for ELT, you’re not just investing in a component—you’re investing in safety. Our cables have been trusted by aviation professionals around the world to keep ELT systems operational when emergencies strike, ensuring that distress signals are transmitted clearly and efficiently, and lives are saved. With FRS, you can have confidence that your ELT system is equipped with the best possible cables, engineered for reliability, performance, and peace of mind.
For all your Aviation Cables for ELT needs, choose FRS—the brand that puts safety first. Contact us today to learn more about our products and how we can support your aviation safety goals.