Aviation Cable in Aircraft Seating Systems: The Unsung Hero of Passenger Comfort and Safety
When passengers settle into their seats for a flight, they expect comfort, functionality, and above all, safety. While the seat cushion, recline mechanism, and in-flight entertainment screen are visible, a critical network of components works tirelessly behind the scenes. Among the most vital, yet often overlooked, elements are the aviation cables within the aircraft seating system. These specialized cables are the literal lifelines enabling movement, communication, and critical safety functions.
Beyond Simple Wiring: The Multifaceted Role of Aviation Cable
Aviation cable in seating systems is far more complex than standard electrical wire. It encompasses a range of specialized cables designed for specific, demanding tasks:
- Control Cable (Mechanical): Often referred to as Bowden cables or push-pull cables, these are the workhorses for seat adjustment. They transmit force from passenger controls (like recline buttons or levers) to the seat’s mechanisms (actuators, latch releases). Precision, low friction, and high tensile strength are paramount for smooth, reliable operation.
- Application: Manual and powered seat recline, lumbar support adjustment, headrest positioning, leg rest deployment (in premium cabins), seat pan tilt.
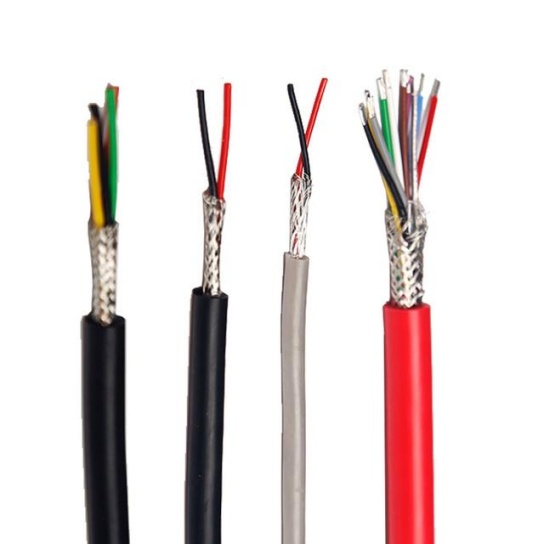
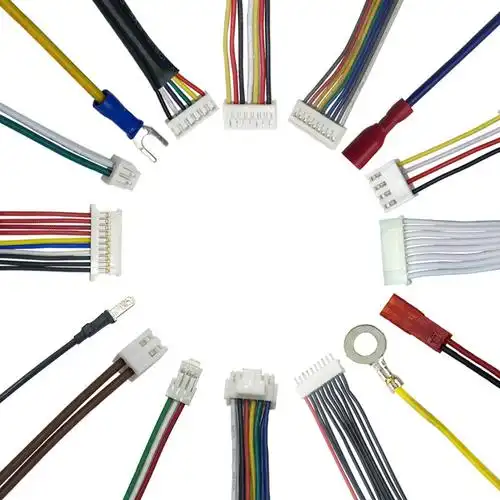
- Electrical Wiring Harness: This intricate network of insulated wires transmits power and data signals throughout the seat.
- Application: Powering seat motors (for recline, lumbar, etc.), in-flight entertainment (IFE) screens and controls, reading lights, USB/power ports, seat occupancy sensors (for Fasten Seatbelt signs), and potentially heating elements or massage functions.
- Safety Cable: Dedicated cables are crucial for critical safety mechanisms.
- Application: Emergency release systems for flight attendant override of recline (especially important for egress in exit rows or during emergencies), positive latching mechanisms for ensuring seats remain upright and locked during takeoff and landing.
Why “Aviation Grade” Matters: Meeting Stringent Requirements
Aircraft operate in an environment unlike any other. Cables within seating systems must adhere to rigorous standards to ensure performance and safety:
- Extreme Lightweight: Every gram counts in aviation. Cables use specialized alloys (like high-strength stainless steel for control cables) and optimized designs to minimize weight without sacrificing strength.
- Exceptional Durability & Fatigue Resistance: Seats undergo constant use – thousands of adjustment cycles, passenger movement, and vibration during flight. Cables must withstand this relentless wear and tear without failing.
- Fire Safety: Flame retardancy and low smoke/toxicity (FST – Fire, Smoke, Toxicity) are non-negotiable. Cables must meet stringent aviation flammability standards (e.g., FAR 25.853, Airbus ABD0031, Boeing BSS 7238/7239) to prevent fire propagation and minimize hazardous smoke in the cabin.
- Temperature Resilience: Cables must perform reliably across a vast temperature range, from the cold of high altitude to potential heat buildup within seat structures.
- Vibration and Shock Resistance: Aircraft experience significant vibration during takeoff, landing, and turbulence. Cables must be securely routed and designed to withstand these forces without chafing, breaking, or causing interference.
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): Electrical wiring must be shielded appropriately to prevent interference with critical aircraft avionics systems.
- Certification & Traceability: Every component, including cables, must be fully traceable and manufactured to approved aviation standards (e.g., AS/EN standards), undergoing rigorous qualification testing.
The Critical Link: Cable Failure and Consequences
The failure of an aviation cable within a seating system can range from a minor inconvenience to a significant safety issue:
- Loss of Function: A broken control cable means a passenger cannot adjust their seat. A failed electrical cable could disable IFE or power ports.
- Operational Disruption: A malfunctioning seat, especially in a critical location like an exit row, can lead to flight delays or even cancellations for repair or replacement.
- Safety Hazard: Failure of a safety-critical cable, like an emergency release mechanism or a seat latching system, poses a direct risk to passenger safety during critical phases of flight or an evacuation. Chafed electrical cables also present a potential fire hazard.
Innovation in Aviation Seating Cables
As seating systems become more sophisticated, so do the cables within them:
- Smart Cables: Integration of sensors within cables for health monitoring (detecting wear, tension changes) is emerging.
- Advanced Materials: Development of even lighter, stronger alloys and composite core cables continues.
- Miniaturization: As seat electronics get smaller and more powerful, wiring harnesses require finer gauge wires and more compact connectors.
- Power over Data Lines: Technologies like Power over Ethernet (PoE) are being explored to simplify wiring for seat electronics.
Conclusion: The Vital Veins of Modern Aircraft Seats
Aviation cable is the essential, though often invisible, infrastructure that breathes life into modern aircraft seating systems. From enabling personalized comfort adjustments to powering entertainment and ensuring critical safety functions, these specialized cables perform under extreme pressure and demanding conditions. Their design, manufacturing, and installation adhere to the highest aerospace standards, reflecting their fundamental role in delivering a safe, comfortable, and functional passenger experience. Understanding the importance of these components highlights the incredible engineering that goes into every detail of an aircraft’s interior. When you next adjust your seat or plug in your device, remember the complex network of aviation cables making it all possible.