Aircraft Cable Assemblies: Trends in Cybersecurity for Manufacturing
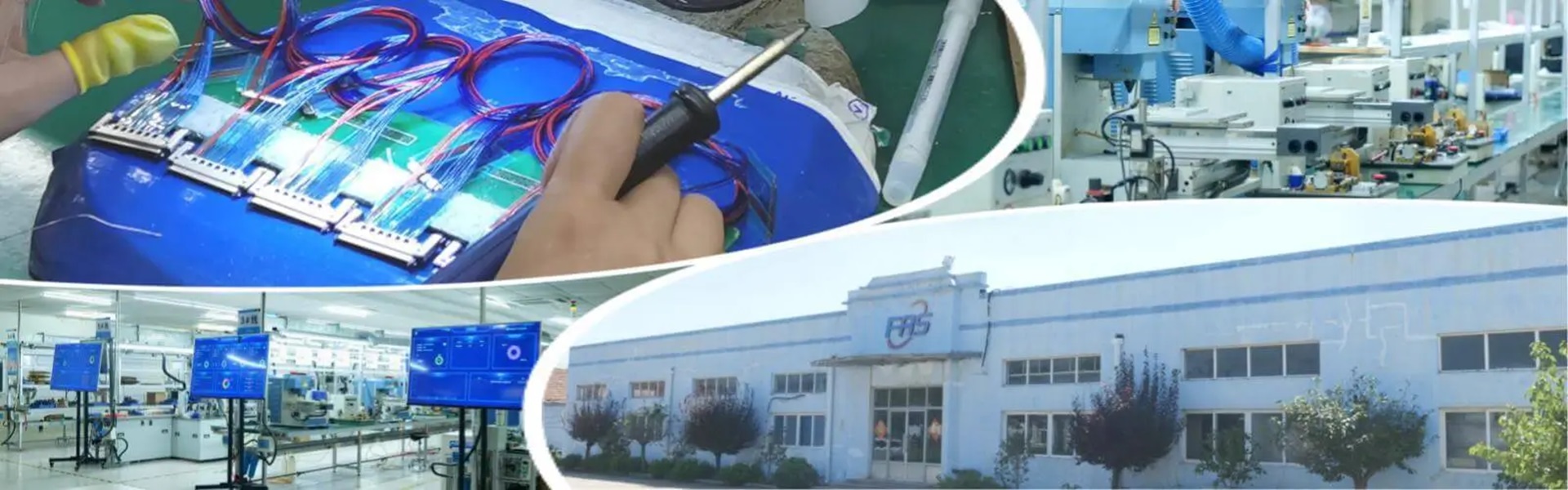
The manufacturing sector of aircraft cable assemblies is a critical link in the global aerospace supply chain, where precision, reliability, and compliance are non-negotiable. As the aerospace industry becomes increasingly digitized—with smart factories, IoT-enabled machinery, and integrated supply chain management systems—cybersecurity has emerged as a paramount concern. Aircraft cable assemblies, which serve as the nervous system of aircraft, transmitting power, data, and control signals across vital systems, demand uncompromising security throughout their manufacturing lifecycle. A single cybersecurity breach in this process could compromise product integrity, lead to costly production delays, or even pose safety risks for end-users. In this context, understanding and adapting to the latest cybersecurity trends is no longer an option but a necessity for manufacturers of aircraft cable assemblies for manufacturing.
1. The Growing Interconnectedness of Aircraft Cable Assembly Manufacturing and Cybersecurity Risks
Modern aircraft cable assembly manufacturing facilities are no longer isolated islands of production. They rely on a complex ecosystem of connected technologies: Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software for engineering specifications, Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) for real-time production monitoring, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems for inventory and order management, and even collaborative platforms that link with suppliers and aerospace OEMs. While this interconnectedness drives efficiency, reduces lead times, and improves quality control for aircraft cable assemblies for manufacturing, it also expands the attack surface for cyber threats.
Cybercriminals target these interconnected systems with a range of tactics. Ransomware attacks, for example, can encrypt critical manufacturing data—such as cable assembly blueprints, material specifications, or production schedules—paralyzing operations until a ransom is paid. Intellectual property (IP) theft is another significant risk: aircraft cable assemblies are engineered with proprietary designs tailored to specific aerospace applications, and stolen IP could lead to counterfeit products entering the supply chain or give competitors an unfair advantage. Additionally, supply chain compromises, where cyber threats infiltrate through third-party suppliers (e.g., material vendors or component manufacturers), can introduce vulnerabilities into the aircraft cable assembly production process without the manufacturer’s knowledge.
For instance, a 2024 report by the Aerospace Industries Association (AIA) noted that 68% of aerospace manufacturers, including those specializing in aircraft cable assemblies, had experienced at least one cyber incident in the past year. Of these incidents, 42% resulted in production downtime averaging 72 hours, and 29% involved the theft of sensitive design data. These statistics underscore the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures in the manufacturing of aircraft cable assemblies for manufacturing.
2. Key Cybersecurity Trends Shaping the Future of Aircraft Cable Assembly Manufacturing
2.1 Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA): “Never Trust, Always Verify”
One of the most impactful trends in cybersecurity for aircraft cable assembly manufacturing is the adoption of Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA). Traditional security models operate on the “trust but verify” principle, assuming that internal networks are safe once access is granted. However, this model is obsolete in today’s interconnected environment, where threats can originate from both external and internal sources.
ZTA flips this paradigm with the mantra “never trust, always verify.” Every user, device, and application attempting to access the manufacturing network—whether an engineer accessing CAD files for aircraft cable assemblies, a machine operator logging into an MES, or a supplier uploading material certifications—must undergo continuous authentication and authorization. This includes multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC), and real-time monitoring of network activity. For aircraft cable assembly manufacturers, ZTA ensures that even if a single point of the network is compromised, the threat is contained, preventing unauthorized access to critical production data or machinery.
Leading aerospace manufacturers have already begun implementing ZTA for their aircraft cable assembly lines. For example, a major OEM reported a 56% reduction in cyber incident response times after deploying ZTA, as the system automatically flagged and isolated suspicious activity before it could impact production.
2.2 Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) Security for Smart Manufacturing
The adoption of IIoT devices is transforming aircraft cable assembly manufacturing into “smart factories.” Sensors embedded in production machinery monitor cable tension, insulation quality, and assembly precision in real time, while connected robots automate repetitive tasks such as crimping or testing. These IIoT devices generate vast amounts of data that manufacturers use to optimize processes and improve product quality for aircraft cable assemblies for manufacturing. However, many IIoT devices lack built-in security features, making them prime targets for cyberattacks.
To address this, manufacturers are investing in IIoT-specific cybersecurity solutions. This includes device hardening (disabling unnecessary ports and protocols), encrypting data transmitted between IIoT devices and central systems, and implementing network segmentation to separate IIoT networks from critical business systems. Additionally, predictive maintenance for IIoT devices—powered by artificial intelligence (AI)—is becoming increasingly common. AI algorithms analyze device performance data to detect anomalies that may indicate a cyber threat, such as unusual data transmission patterns or unexpected software updates.
For aircraft cable assembly manufacturers, securing IIoT devices is not just about protecting production lines; it’s about ensuring the integrity of the data used to quality-check cable assemblies. If IIoT sensors are compromised, the data they collect—such as whether a cable meets tensile strength requirements—could be falsified, leading to non-compliant products entering the aerospace supply chain.
2.3 AI-Powered Threat Detection and Response
Artificial intelligence and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing cybersecurity in aircraft cable assembly manufacturing. Traditional threat detection systems rely on pre-defined rules to identify known threats, but they often fail to detect emerging or zero-day attacks. AI-powered systems, by contrast, learn from historical data and real-time network activity to identify patterns that indicate potential threats—even those that have never been seen before.
In the context of aircraft cable assembly manufacturing, AI can be used to monitor a wide range of activities: from unusual login attempts to CAD software, to unexpected changes in production parameters (e.g., a sudden increase in cable rejection rates due to tampered testing equipment). AI systems can also automate response actions, such as isolating a compromised device or alerting cybersecurity teams, reducing the time between threat detection and mitigation.
A case study from a leading aircraft cable assembly manufacturer found that integrating AI into their cybersecurity strategy reduced false positive alerts by 78% and enabled the team to respond to genuine threats 40% faster. This not only improved security but also minimized disruptions to production, ensuring that aircraft cable assemblies for manufacturing were delivered on time and to specification.
2.4 Compliance-Driven Cybersecurity: Aligning with Aerospace Regulations
The aerospace industry is one of the most heavily regulated sectors in the world, and manufacturers of aircraft cable assemblies for manufacturing must comply with strict cybersecurity standards. These include the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 27001, which sets requirements for information security management systems, and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework, which provides guidelines for identifying, protecting, detecting, responding to, and recovering from cyber threats.
In addition to these general standards, aerospace-specific regulations—such as the European Union’s Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) Regulation (EU) 2018/1139 and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA)’s Cybersecurity Risk Management Guidance—impose additional requirements on manufacturers. These regulations mandate that manufacturers implement cybersecurity measures throughout the product lifecycle, from design and production to maintenance and disposal of aircraft cable assemblies.
Compliance is not just a legal obligation; it’s a competitive differentiator. Aerospace OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers increasingly require their partners to demonstrate robust cybersecurity compliance before awarding contracts. Manufacturers that invest in compliance-driven cybersecurity not only avoid costly fines and reputational damage but also position themselves as trusted suppliers of aircraft cable assemblies for manufacturing.
3. The Impact of Cybersecurity on Aircraft Cable Assembly Quality and Reliability
Cybersecurity is not just a technical issue—it directly impacts the quality and reliability of aircraft cable assemblies. A cyber breach that tampers with production data or machinery can result in cable assemblies that fail to meet aerospace standards. For example, if a hacker alters the specifications in a CAD file for a high-performance aircraft cable, the resulting product may not withstand the extreme temperatures, vibrations, or pressure changes encountered during flight, posing a severe safety risk.
Moreover, cybersecurity breaches can disrupt quality control processes. Many aircraft cable assembly manufacturers use automated testing systems to verify electrical conductivity, insulation resistance, and mechanical strength. If these systems are compromised, they may produce false pass/fail results, allowing defective cables to enter the supply chain. This not only leads to costly recalls but also erodes customer trust in the manufacturer’s products.
By contrast, robust cybersecurity measures enhance quality and reliability. Secure access controls ensure that only authorized personnel can modify design or production parameters. Real-time threat detection prevents tampering with testing equipment. And compliance with regulations ensures that aircraft cable assemblies are manufactured to the highest standards of safety and performance.
4. FRS: Your Trusted Partner for Secure Aircraft Cable Assemblies for Manufacturing
In an era where cybersecurity is integral to manufacturing excellence, FRS stands out as a leading provider of aircraft cable assemblies for manufacturing. With decades of experience in the aerospace industry, FRS understands the unique cybersecurity challenges facing manufacturers and has integrated the latest security trends into every aspect of its operations.
At FRS, we have implemented a comprehensive Zero Trust Architecture to protect our manufacturing network, ensuring that every access request—whether from our in-house engineers, production teams, or supply chain partners—is rigorously authenticated and authorized. Our smart factories are equipped with state-of-the-art IIoT security solutions, including encrypted data transmission, network segmentation, and AI-powered predictive maintenance, to safeguard our production machinery and the critical data they generate. We also leverage AI-driven threat detection systems to monitor our operations 24/7, enabling us to detect and mitigate potential threats before they impact production.
Compliance is at the core of FRS’s cybersecurity strategy. We are fully certified to ISO 27001 and align with NIST, EASA, and FAA cybersecurity regulations, ensuring that our aircraft cable assemblies meet the strictest industry standards. Our commitment to compliance is not just about meeting legal requirements; it’s about delivering products that our customers can trust to be safe, reliable, and secure.
FRS’s aircraft cable assemblies are engineered with precision and manufactured in a secure environment, making them the ideal choice for aerospace OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers. Whether you need custom cable assemblies for commercial aircraft, military jets, or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), FRS has the expertise, technology, and security measures to deliver solutions that exceed your expectations.
Choose FRS as your partner for aircraft cable assemblies for manufacturing, and experience the peace of mind that comes with working with a manufacturer that prioritizes cybersecurity, quality, and reliability. Contact us today to learn more about how we can support your aerospace production needs.