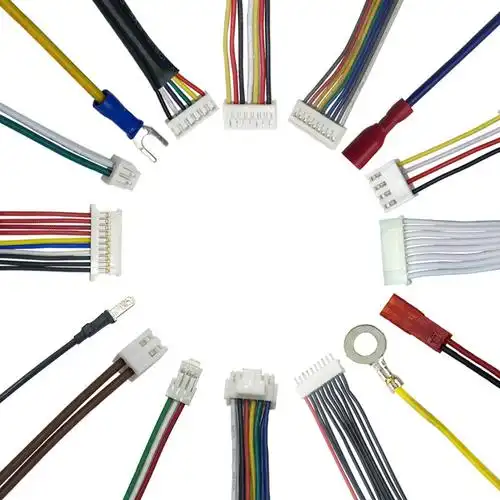
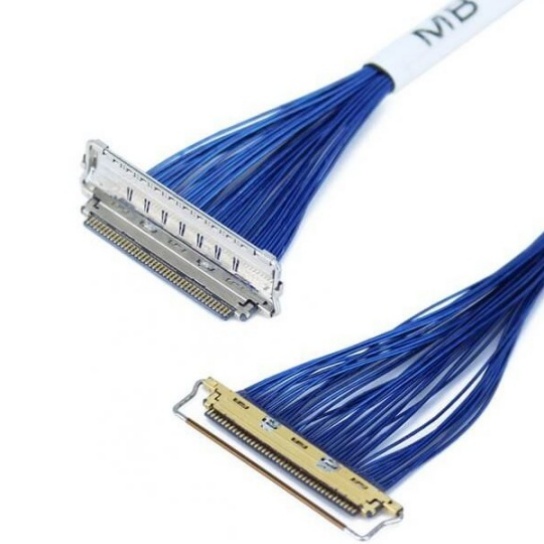
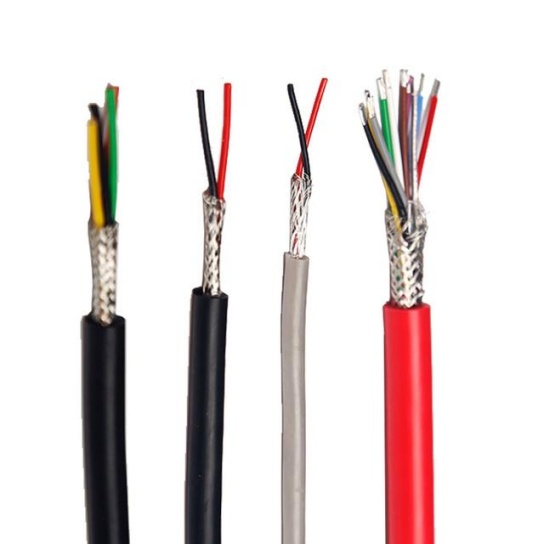
Aircraft Cable Assemblies: Compliance with EASA Standards
In the global aviation industry, safety and reliability are non-negotiable priorities, and aircraft cable assemblies play a critical role in ensuring the seamless operation of vital systems—from flight controls to avionics and power distribution. Among the numerous regulatory frameworks governing aviation components, the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) standards stand out as a benchmark for excellence, setting rigorous criteria to mitigate risks and uphold operational integrity. For manufacturers, suppliers, and operators alike, understanding and adhering to EASA standards for aircraft cable assemblies is not just a legal obligation but a cornerstone of maintaining trust in the aviation ecosystem.
The Core EASA Standards Governing Aircraft Cable Assemblies
EASA’s regulatory oversight for aircraft components is primarily rooted in its Certification Specifications (CS) and Guidance Materials (GM), which align with international standards such as those from the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). For aircraft cable assemblies, key EASA standards include:
- CS-25 (Certification Specification for Large Aeroplanes): This standard outlines requirements for the design and installation of electrical systems, including cable assemblies. It mandates that cables must withstand extreme environmental conditions—such as temperature fluctuations (-65°C to +125°C for most applications), humidity, vibration, and exposure to fluids like jet fuel and hydraulic oil—without compromising performance.
- CS-23 (Certification Specification for Normal, Utility, Aerobatic, and Commuter Category Aeroplanes): Applicable to smaller aircraft, CS-23 imposes similar but scaled requirements for cable assemblies, focusing on weight efficiency without sacrificing safety. It emphasizes proper routing and shielding to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can disrupt sensitive avionics.
- DO-160 (Environmental Conditions and Test Procedures for Airborne Equipment): While developed by RTCA, EASA recognizes DO-160 as a critical test standard for cable assemblies. It includes rigorous testing protocols for EMI/radio frequency interference (RFI) immunity, voltage withstand, insulation resistance, and mechanical durability (e.g., flexing and abrasion resistance).
Key Compliance Requirements for Manufacturers
Achieving EASA compliance for aircraft cable assemblies requires manufacturers to implement end-to-end quality control processes, from material selection to final testing. Here are the critical steps:
- Material Qualification: All materials used in cable assemblies—including conductors (typically copper or copper alloys), insulators (PTFE, FEP, or silicone), and connectors—must meet EASA-approved specifications. For example, insulators must be flame-retardant and low-smoke to minimize fire hazards, as per EASA’s CS-25.853 requirement for fire protection.
- Precision Manufacturing: Production processes must adhere to strict tolerances to ensure consistent performance. This includes controlled crimping of connectors (to avoid signal loss or electrical resistance), proper stripping of insulation (to prevent conductor damage), and automated testing of continuity and insulation resistance during assembly.
- Documentation and Traceability: EASA mandates comprehensive documentation, including a Technical File (TCF) for each cable assembly type. The TCF must include material certificates, test reports, design schematics, and traceability records (e.g., batch numbers for materials and production dates) to enable full accountability throughout the component’s lifecycle.
- Post-Production Testing: Every batch of cable assemblies must undergo rigorous testing to validate compliance. This includes environmental testing (temperature, humidity, vibration), electrical testing (continuity, insulation resistance, EMI shielding effectiveness), and mechanical testing (pull strength for connectors, flex life).
Risks of Non-Compliance
Failing to meet EASA standards can have severe consequences for all stakeholders. For manufacturers, non-compliance may result in product recalls, fines, or revocation of EASA Part 21G production approval—effectively halting operations. For operators, using non-compliant cable assemblies increases the risk of in-flight failures, such as electrical shorts, signal interference, or even fires, which can lead to catastrophic accidents, loss of life, and reputational damage. Additionally, non-compliant components may not be accepted in European and global markets that recognize EASA certifications, limiting market access for airlines and suppliers.
Choosing a Compliant Supplier: The FRS Advantage
When selecting a supplier for aircraft cable assemblies, EASA compliance should be the top priority. FRS, a leading manufacturer of aviation cable assemblies, stands out as a trusted partner for global aviation customers, thanks to its unwavering commitment to EASA standards.
FRS operates state-of-the-art facilities certified to EASA Part 21G and ISO 9001/AS9100, ensuring every cable assembly is designed, manufactured, and tested to meet CS-25, CS-23, and DO-160 requirements. With a team of experienced engineers and quality specialists, FRS offers custom cable solutions tailored to specific aircraft applications, backed by full traceability and comprehensive technical documentation. Whether for commercial airliners, military aircraft, or general aviation, FRS delivers reliable, compliant cable assemblies that keep aviation systems running safely. Choose FRS—where EASA compliance is built into every wire.